News + Articles
Can a dental bridge be removed and recemented?
Yes, our dentist can remove and recement your dental bridge if the bridge is still in good condition and your supporting teeth are healthy.
To fully appreciate why these conditions are so important, it’s essential to first understand how a dental bridge is designed to function.
Below, we cover the basics of what a bridge does and why its components are key to its longevity.
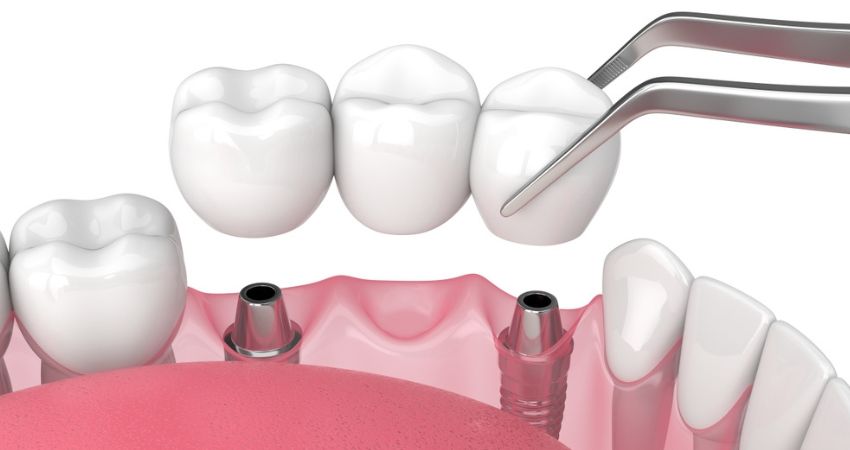
Understanding the Role of a Dental Bridge
A dental bridge offers a fixed, long-term solution for replacing missing teeth. This restoration works by anchoring an artificial tooth (called a pontic) to the adjacent teeth or implants.
For a bridge to work well and last, it needs a strong bond from dental cement. It also depends on the health of the supporting abutment teeth.
Common Types of Dental Bridges
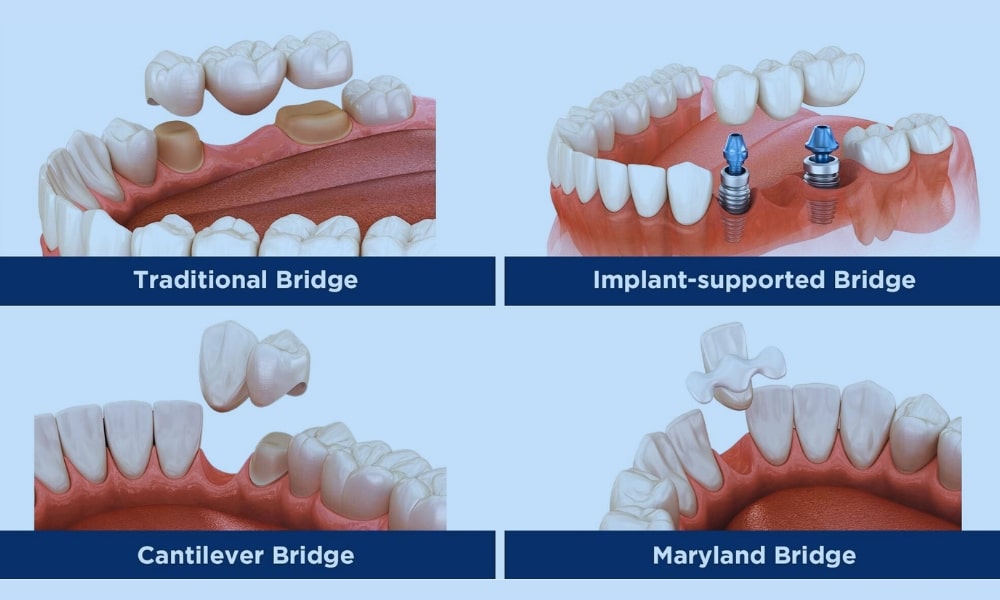
There are several types of dental bridges, each with a unique design:
- A traditional dental bridge uses dental crowns placed on the abutment teeth on both sides of the gap to support a pontic.
- A Maryland bridge bonds to the back of adjacent teeth using metal or porcelain wings.
- A cantilever bridge relies on a single abutment tooth, making it ideal when support is available on only one side.
- An implant-supported bridge uses titanium implants that a surgeon surgically embeds in the jawbone for support, rather than using natural teeth.
Knowing which type of bridge you have is essential for determining whether it can be removed and safely recemented.
When Can a Dental Bridge Be Removed and Recemented?
It is often possible for a dentist to remove and recement a dental bridge. This procedure can be a cost-effective way to restore comfort, oral function, and bite stability when the original bridge is still in good shape.
However, this is only recommended when several key clinical conditions are met. Your dentist will evaluate the following factors:
1. The Bridge Must Be Structurally Intact
Your dentist will inspect the bridge to ensure it is free from cracks, stress fractures, worn porcelain, or other significant damage. A structurally sound bridge is the primary candidate for recementation.
2. The Abutment Teeth Must Be Healthy
The supporting teeth (abutments) must be strong, stable, and free from decay or periodontal (gum) disease. Healthy teeth are essential for securely supporting the recemented bridge long-term.
3. The Bridge Must Still Fit Properly
The bridge must fit accurately on the teeth, align well with your bite, and feel stable during chewing. A proper fit is crucial to prevent future issues and ensure comfort.
4. A Clean Bonding Surface
The inner surface of the bridge must be completely clean and free of old cement and debris. This is critical for allowing the new dental cement to form a strong, effective bond.
5. A Stable and Favorable Bite
Your overall bite force needs to be stable and balanced, ensuring that no excessive stress is placed on the recemented bridge, which could cause it to loosen again.
Based on a thorough dental examination, your dentist will assess all these factors to determine if removal and recementation are the best treatment options for your case.
When Recementation Isn’t Enough
In some cases, a dentist may suggest removing the bridge and replacing it with a new one. This is especially true if there is structural damage or biological issues.
Tooth Decay or Infection Beneath the Bridge
If the abutment teeth develop decay or infection, the bridge must be removed so your dentist can provide root canal treatment or other necessary therapy. After treatment, your dentist will determine whether to reuse or replace the bridge.
Damaged Bridge Framework
Chips, cracks, or worn porcelain may reduce the bridge’s strength and aesthetic appearance. In these cases, full replacement with a new prosthesis is usually recommended.
Poor Fit or Ongoing Instability
If the bridge consistently feels loose, causes bite misalignment, or shifts while chewing, a completely new bridge may be necessary to restore comfort and function.
How Dentists Remove a Dental Bridge
Step 1: Assessment and Planning
Your dentist begins with a clinical exam and dental X-rays to evaluate the bridge’s position and bonding.
Step 2: Gentle Removal Using Leverage
Dentists use special dental instruments to carefully lift the bridge. They apply steady pressure so that surrounding teeth and gum tissue remain safe.
Step 3: Mechanical Sectioning (If Needed)
If the bridge is too tightly bonded, your dentist cuts a precise slot into the framework using a dental drill. This allows the internal cement seal to be broken from within.
Step 4: Local Anesthesia for Comfort
If needed, local anesthesia ensures you remain comfortable during the procedure.
Important: Never attempt to remove the bridge at home. Doing so can damage the bridge, your natural teeth, or the surrounding soft tissues.
Can All Types of Dental Bridges Be Recemented?
Not every dental bridge can be safely removed and reused. Whether recementation is possible depends on the bridge’s design, how it attaches to your teeth or implants, and its current condition.
To help you understand the differences, the table below compares the main types of dental bridges and shows how likely each can be recemented.
Bridge Type | Recementable | Details |
Traditional Bridge | Often | Supported by crowns on both sides. Commonly recemented if teeth are healthy. |
Maryland Bridge | Sometimes | Bonded with wings; smaller surface area may limit long-term adhesion. |
Cantilever Bridge | Rarely | Supported by one tooth; often unstable and replaced rather than reused. |
Implant-Supported Bridge | Not typically | Anchored into the jawbone; requires surgical removal and cannot be recemented. |
👉 Don’t wait for the pain to get worse — Schedule an appointment with our dentist today and take the first step toward a healthier smile!
Risks of Removing and Recementing a Dental Bridge
While recementing a bridge is often effective, some risks may affect long-term results.
Risk 1: Damage to Bridge or Nearby Teeth
If the bridge is tightly bonded, removal may place stress on the abutment teeth or cause fractures in the porcelain. Dentists use special tools to reduce this risk.
Risk 2: Weak Bond After Recementing
Over time, the bonding surface may wear down. This can reduce how well the new dental cement holds, leading to earlier loosening.
Risk 3: Recurrent Loosening
If bite misalignment or tooth shifting caused the original failure, and it’s not corrected, the bridge may become loose again after recementation.
Risk 4: Hidden Decay or Gum Infection
Decay or gum disease beneath the bridge must be treated before reuse. If untreated, these issues can compromise the stability and lead to bridge failure.
How Long Does a Recemented Dental Bridge Last?
A recemented bridge typically lasts 3 to 7 years, depending on:
- Oral Hygiene: Daily brushing, flossing with a floss threader, and professional dental cleanings.
- Bite Force: Teeth grinding (bruxism) can shorten a bridge’s functional lifespan.
- Age and Material: Older restorations or weaker materials often bond less effectively when reused.
With proper care, a recemented bridge can serve you reliably for many years.
Alternatives When Your Bridge Cannot Be Recemented
If your dental bridge can’t be safely reused, your dentist may recommend a long-term alternative:
- Replace it with a new bridge: Custom-built bridges restore bite alignment and esthetics.
- Consider dental implants: Implant-supported bridges provide stability without relying on neighboring teeth.
- Use a temporary bridge: Maintains chewing function and prevents shifting until permanent restoration is ready.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does removing a bridge hurt?
No. The procedure is generally painless, and local anesthesia ensures comfort.
Can I remove a dental bridge at home?
No. Attempting self-removal risks serious injury and damage.
Can a bridge be reused after removal?
Yes, if the bridge is intact, fits well, and the supporting structures are healthy, your dentist may recommend recementation.

Dr. Ronald Pham, DDS, is a Doctor of Dental Surgery who graduated from the USC Ostrow School of Dentistry in 2015. With over 8 years of experience in restorative dentistry, including dental implants, crowns, bridges, fillings, root canals…
Dr. Pham has restored the smiles of +2,000 patients and is committed to providing professional dental care focused on patient comfort. He achieves this by combining a welcoming space and state-of-the-art dental technology.

Guaranteed Smiles!
As a premiere dentist office in Orange CA, we will always make sure that your experience is memorable, friendly, and professional. We strive to meet your highest expectations in every way imaginable, from your very first interaction with our office staff, to the quality of treatment you receive. We don’t take our patients’ trust for granted, and will promise to over-deliver with your best interest in mind. So give us a call today, and experience our first-class service!
Insurance
Accepted
We proudly accept most dental insurance plans, and welcome cash patients as well. Call us today for more information.
$199
Special
New to our dental office? Take advantage of our New Patient special offer with x-rays, exam, and full report of findings.
Extended
Hours
Do you have an emergency? Need to see us a little later or earlier? Let us know. We can be flexible to meet your busy schedule!
